MPI_Type_create_struct
Create an MPI datatype from a general set of datatypes, displacements, and block sizesint MPI_Type_create_struct( int count, int array_of_blocklengths[], MPI_Aint array_of_displacements[], MPI_Datatype array_of_types[], MPI_Datatype *newtype );
Parameters
- count
- [in] number of blocks (integer) --- also number of entries in arrays array_of_types, array_of_displacements and array_of_blocklengths
- array_of_blocklength
- [in] number of elements in each block (array of integer)
- array_of_displacements
- [in] byte displacement of each block (array of integer)
- array_of_types
- [in] type of elements in each block (array of handles to datatype objects)
- newtype
- [out] new datatype (handle)
Remarks
MPI_TYPE_CREATE_STRUCT is the most general type constructor. It further generalizes the previous one in that it allows each block to consist of replications of different datatypes.
Example: Let type1 have type map,
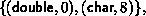
with extent 16. Let B = (2, 1, 3), D = (0, 16, 26), and T = (MPI_FLOAT, type1, MPI_CHAR). Then a call to MPI_TYPE_STRUCT(3, B, D, T, newtype) returns a datatype with type map,
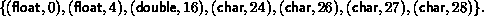
That is, two copies of MPI_FLOAT starting at 0, followed by one copy of type1 starting at 16, followed by three copies of MPI_CHAR, starting at 26. (We assume that a float occupies four bytes.)
In general, let T be the array_of_types argument, where T[i] is a handle to,
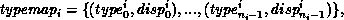
with extent exi. Let B be the array_of_blocklength
argument and D be the array_of_displacements argument.Let c be the count
argument. Then the newly created datatype has a type map with
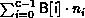
entries:
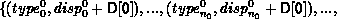
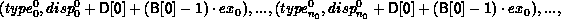
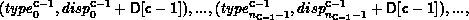
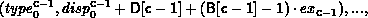
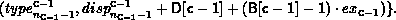
A call to MPI_TYPE_CREATE_HINDEXED( count, B, D, oldtype, newtype) is equivalent to a call to MPI_TYPE_CREATE_STRUCT( count, B, D, T, newtype), where each entry of T is equal to oldtype.
Thread and Interrupt Safety
This routine is thread-safe. This means that this routine may be safely used by multiple threads without the need for any user-provided thread locks. However, the routine is not interrupt safe. Typically, this is due to the use of memory allocation routines such as malloc or other non-MPICH runtime routines that are themselves not interrupt-safe.
Notes for Fortran
All MPI routines in Fortran (except for MPI_WTIME and MPI_WTICK) have an additional argument ierr at the end of the argument list. ierr is an integer and has the same meaning as the return value of the routine in C. In Fortran, MPI routines are subroutines, and are invoked with the call statement.All MPI objects (e.g., MPI_Datatype, MPI_Comm) are of type INTEGER in Fortran.
Errors
All MPI routines (except MPI_Wtime and MPI_Wtick) return an error value; C routines as the value of the function and Fortran routines in the last argument. Before the value is returned, the current MPI error handler is called. By default, this error handler aborts the MPI job. The error handler may be changed with MPI_Comm_set_errhandler (for communicators), MPI_File_set_errhandler (for files), and MPI_Win_set_errhandler (for RMA windows). The MPI-1 routine MPI_Errhandler_set may be used but its use is deprecated. The predefined error handler MPI_ERRORS_RETURN may be used to cause error values to be returned. Note that MPI does not guarentee that an MPI program can continue past an error; however, MPI implementations will attempt to continue whenever possible.
- MPI_SUCCESS
- No error; MPI routine completed successfully.
- MPI_ERR_ARG
- Invalid argument. Some argument is invalid and is not identified by a specific error class (e.g., MPI_ERR_RANK).
- MPI_ERR_TYPE
- Invalid datatype argument. May be an uncommitted MPI_Datatype (see MPI_Type_commit).
Example Code
The following sample code illustrates MPI_Type_create_struct.
#include "mpi.h"#include <stdio.h>
struct Partstruct
{
char c;
double d[6];
char b[7];
};
int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
struct Partstruct particle[1000];
int i, j, myrank;
MPI_Status status;
MPI_Datatype Particletype;
MPI_Datatype type[3] = { MPI_CHAR, MPI_DOUBLE, MPI_CHAR };
int blocklen[3] = { 1, 6, 7 };
MPI_Aint disp[3];
MPI_Init(&argc, &argv);
disp[0] = &particle[0].c - &particle[0];
disp[1] = &particle[0].d - &particle[0];
disp[2] = &particle[0].b - &particle[0];
MPI_Type_create_struct(3, blocklen, disp, type, &Particletype);
MPI_Type_commit(&Particletype);
MPI_Comm_rank(MPI_COMM_WORLD, &myrank);
if (myrank == 0)
{
MPI_Send(particle, 1000, Particletype, 1, 123, MPI_COMM_WORLD);
}
else if (myrank == 1)
{
MPI_Recv(particle, 1000, Particletype, 0, 123, MPI_COMM_WORLD, &status);
}
MPI_Finalize();
return 0;
}
DOWNLOAD
Win32 DeinoMPI.2.0.1.msi
Win64 DeinoMPI.x64.2.0.1.msi