MPI_Type_contiguous
Creates a contiguous datatypeint MPI_Type_contiguous( int count, MPI_Datatype old_type, MPI_Datatype *new_type_p );
Parameters
- count
- [in] replication count (nonnegative integer)
- oldtype
- [in] old datatype (handle)
- newtype
- [out] new datatype (handle)
Remarks
Contiguous The simplest datatype constructor is MPI_TYPE_CONTIGUOUS which allows replication of a datatype into contiguous locations.
newtype is the datatype obtained by concatenating count copies of oldtype. Concatenation is defined using extent as the size of the concatenated copies.
Example Let oldtype have type map 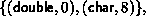 with
extent 16, and let
with
extent 16, and let 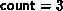 . The type map of the datatype
returned by newtype is
. The type map of the datatype
returned by newtype is
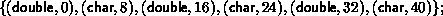
i.e., alternating double and char elements, with displacements 0, 8, 16, 24, 32, 40.
In general, assume that the type map of oldtype is
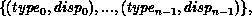
with extent ex. Then newtype has a type map with
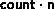 entries defined by:
entries defined by:
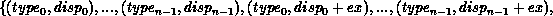
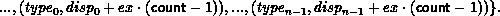
Thread and Interrupt Safety
This routine is thread-safe. This means that this routine may be safely used by multiple threads without the need for any user-provided thread locks. However, the routine is not interrupt safe. Typically, this is due to the use of memory allocation routines such as malloc or other non-MPICH runtime routines that are themselves not interrupt-safe.
Notes for Fortran
All MPI routines in Fortran (except for MPI_WTIME and MPI_WTICK) have an additional argument ierr at the end of the argument list. ierr is an integer and has the same meaning as the return value of the routine in C. In Fortran, MPI routines are subroutines, and are invoked with the call statement.All MPI objects (e.g., MPI_Datatype, MPI_Comm) are of type INTEGER in Fortran.
Errors
All MPI routines (except MPI_Wtime and MPI_Wtick) return an error value; C routines as the value of the function and Fortran routines in the last argument. Before the value is returned, the current MPI error handler is called. By default, this error handler aborts the MPI job. The error handler may be changed with MPI_Comm_set_errhandler (for communicators), MPI_File_set_errhandler (for files), and MPI_Win_set_errhandler (for RMA windows). The MPI-1 routine MPI_Errhandler_set may be used but its use is deprecated. The predefined error handler MPI_ERRORS_RETURN may be used to cause error values to be returned. Note that MPI does not guarentee that an MPI program can continue past an error; however, MPI implementations will attempt to continue whenever possible.
- MPI_SUCCESS
- No error; MPI routine completed successfully.
- MPI_ERR_TYPE
- Invalid datatype argument. May be an uncommitted MPI_Datatype (see MPI_Type_commit).
- MPI_ERR_COUNT
- Invalid count argument. Count arguments must be non-negative; a count of zero is often valid.
- MPI_ERR_INTERN
- This error is returned when some part of the MPICH implementation is unable to acquire memory.
Example Code
The following sample code illustrates MPI_Type_contiguous.
#include "mpi.h"#include <stdio.h>
int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
int myrank;
MPI_Status status;
MPI_Datatype type;
int buffer[100];
MPI_Init(&argc, &argv);
MPI_Type_contiguous( 100, MPI_CHAR, &type );
MPI_Type_commit(&type);
MPI_Comm_rank(MPI_COMM_WORLD, &myrank);
if (myrank == 0)
{
MPI_Send(buffer, 1, type, 1, 123, MPI_COMM_WORLD);
}
else if (myrank == 1)
{
MPI_Recv(buffer, 1, type, 0, 123, MPI_COMM_WORLD, &status);
}
MPI_Finalize();
return 0;
}
DOWNLOAD
Win32 DeinoMPI.2.0.1.msi
Win64 DeinoMPI.x64.2.0.1.msi